|
GR9677 #39
|
|
|
Problem
|
|
|
This problem is still being typed. |
Atomic }Ionization Potential }Ionization Potential
Atoms with full shells have high ionization potentials---they would hardly want to lose an electron, and thus it would take a great amount of energy to ionize them. Atoms with close-to-full-shells have similarly high potentials, as compared to atoms that are in the middle of the spectrum, take 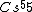 , for example. , for example.
(A) He has a full orbital, and thus its ionization potential must be high.
(B) N has a close-to-full orbital.
(C) O has a close-to-full orbital.
(D) Ar is a nobel gas, and thus its orbital is full.
(E) This is it. Cs has the lowest IP of all (of the above).
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
ramparts
2009-09-26 11:18:26 | I had a similar solution as mike's - I just didn't explain it to myself as well (not remembering much of this chem stuff) :) The outer electrons in Cs are way farther from the nucleus than in the other atoms, so you'd expect the ionization potential to be lowest there. It's true, there might be countervening effects from the number of electrons in the outer orbital, but I would imagine that, as is the case here, ETS would give you the answer that matches both of those criteria, rather than making you balance one against the other :) |  |
|
|
Comments |
capoo0819
2017-10-26 12:54:10 | (D) Ar is a nobel gas\\\\r\\\\n->Should be \\\\\\\"noble\\\\\\\"... |  | kevintah
2015-10-10 17:53:06 | The way I thought about it is that the bigger the atom is, the more the shielding, and thus an electron can easily leave, thus CS. |  | ramparts
2009-09-26 11:18:26 | I had a similar solution as mike's - I just didn't explain it to myself as well (not remembering much of this chem stuff) :) The outer electrons in Cs are way farther from the nucleus than in the other atoms, so you'd expect the ionization potential to be lowest there. It's true, there might be countervening effects from the number of electrons in the outer orbital, but I would imagine that, as is the case here, ETS would give you the answer that matches both of those criteria, rather than making you balance one against the other :)
noether
2009-11-05 10:59:17 |
I would hope so.
|
maxdp
2013-09-25 20:22:53 |
Looking at mikewofsey's link, and the graph on that page, it seems clear that a good rule of thumb is that anything in the right half of the first few rows is always going to have a higher Ionization Pressure than any element in rows 5+. So for this problem, really all you needed was the approximate columns the first four elements were in.
|
|  | f4hy
2009-04-03 14:30:59 | Cs is an alkali metal. The alkali metals are the far left column of the periodic table and have one electron more than a noble gas. Because of this one valance electron they give it up very easily and the IP is very low.
The alkali metals explode when placed in water, the farther down the table you go the more reactive.
maxdp
2013-09-25 20:18:58 |
I was about to comment that it's ridiculous to be expected to remember where Cs is horizontally on the periodic table, but then I realized you can just subtract the numbers of each orbital (length of each row of the table) to find out.
54-2-8-8-16-16 = 1
So it's in the first column.
|
|  | mikewofsey
2006-03-22 16:37:11 | Hi Yosun, the biggest factor influencing the ionization potential is the electrostatic attraction to the nucleus, and more inner rings of electrons tend to shield the electron from the Coulombic attraction, as well as slightly increasing the inverse-square radius. So, there is some left-right periodic table effect on this, but the biggest effect is going DOWN the periodic table. Cs is a larger atom, the outer electrons are more weakly bound due to the reasons listed above. A short discussion on this can be found here: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionization_potential
saar
2014-04-01 03:32:04 |
Thanks! The graph on that page states the relationship between the atomic number and ionisation energy clearly
|
|  |
|
| Post A Comment! |
|
|
Bare Basic LaTeX Rosetta Stone
|
LaTeX syntax supported through dollar sign wrappers $, ex., $\alpha^2_0$ produces 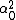 . .
|
| type this... |
to get... |
| $\int_0^\infty$ |
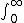 |
| $\partial$ |
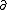 |
| $\Rightarrow$ |
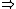 |
| $\ddot{x},\dot{x}$ |
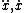 |
| $\sqrt{z}$ |
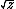 |
| $\langle my \rangle$ |
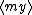 |
| $\left( abacadabra \right)_{me}$ |
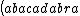_{me}) |
| $\vec{E}$ |
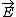 |
| $\frac{a}{b}$ |
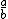 |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
