|
GR8677 #6
|
|
|
Problem
|
|
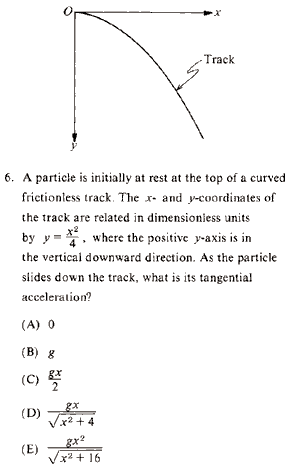 |
Mechanics }Vectors }Vectors
Since there is only one force acting, i.e., the gravitational force, one can find the tangential acceleration by projecting 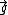 in the tangential direction. Equivalently, one dots gravity with the tangential unit vector, in the tangential direction. Equivalently, one dots gravity with the tangential unit vector, 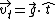 . .
There's a long way to do this, wherein one writes out the full Gibbsean vector formalism, and then there's a short and elegant way. (The elegant solution is due to Teodora Popa.)
The problem gives  = y = x^2/4) . Thus, . Thus, 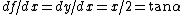 , where in the last step, one notes that the ratio , where in the last step, one notes that the ratio 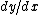 forms the tangent of the indicated angle. forms the tangent of the indicated angle.
One recalls the Pythagorean identity 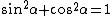 , and the definition of , and the definition of 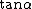 in terms of in terms of 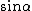 and and 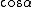 . Thus, one gets . Thus, one gets 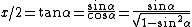 . Square both sides to get . Square both sides to get 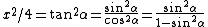 . .
Solve 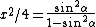 to get to get 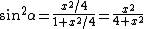 . .
The angle between the vectors  and and  is is 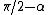 , and thus the tangential acceleration is , and thus the tangential acceleration is 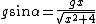 . .
Beautiful problem.
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
pranav
2012-11-02 22:23:53 | (same concept as one given...but simpler math)
Differentiating y w.r.t x gives:
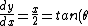)
Draw a right triangle, with one angle 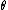 . .
Now label the side adjacent as "2", opposite as "x".
The hypotenuse becomes 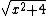 . .
Now we want the tangential acceleration, which would be the "g" multiplied by the cosine of the angle opposite to 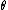 i.e. i.e. 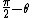 , since , since 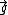 is downward parallel to the side we labeled "x" (i.e. the dot product basically) is downward parallel to the side we labeled "x" (i.e. the dot product basically)
Therefore, answer is:
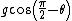 = g sin(\theta) = g \frac{(opposite)}{(hypotenuse)} = \frac{g x}{\sqrt{x^2+4}})
(D) |  | malianil
2011-11-05 05:52:47 | For those who are not inclined to solve it with trigonometric functions can take a snapshot drawing of the force diagram at arbitrary location (y,x) where rn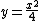 and then use euclidean geometry to find our that the Force component of the tangent is a function of x and is rn and then use euclidean geometry to find our that the Force component of the tangent is a function of x and is rn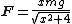 rnIt is simpler this way for me. rnIt is simpler this way for me. |  | nakib
2010-04-02 11:51:51 | (A) Lol!
(B) Of course not! The tangent is not pointing downwards.
(C) Wrong units.
(D) Right units, maybe correct. Also, 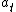 goes to goes to 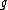 as as  goes to goes to  . .
(E) Wrong units.
(D) is the answer.
The rigorous solutions are beautiful, but are not feasible under GRE exam conditions...
Shahbaz Ahmed Chughtai
2012-06-09 22:51:44 |
Very Nice. GRE is designed to use common sense !!!
But I salute the website owners for such a hard work !
|
|  | p3ace
2008-05-15 06:11:52 | I apologize for what I just said. It came out wrong and I feel terrible after having reread it. What I meant to say was, if you want to know how to just crank out the answer, this is how I would do it. |  | p3ace
2008-05-15 06:08:15 | The process of elimination is great in a pinch on a test but it doesn't demonstrate any physics, or in this case math.
To me the most straight forward way to do this is:
The tangential direction is just the direction of r vector,
r=ix+jy=ix+j(x^2)/4.
r hat or the unit vector in the tangential direction is just r/magnitude, i.e.
r hat = [ix+j(x^2)/4]/{x^2+[(x^2)/4)]^2}^(1/2)
You can factor an x out of the denominator and cancel it with the x in the numerator, leaving
r hat = (i+jx/4)/[1+(x^2)/16]^(1/2)
Now dot the acceleration vector, a=jg with the unit vector in the tangential direction to get the tangential acceleration,
a tangential = g[(x/4)/(1+x^2/16)].
Now, to get the form in the answer, multiply through in the denominator by the 4. Inside the radical, it becomes a 16 so that you have,
a tangential = gx/[16+x^2)^(1/2), Wah, LA, choice D.
Sorry I'm not a latex jockey. To me this is radically simple, more so than the other solutions, just because this is what makes sense to me. I know that others see it differently and whatever works for you is a okay, so this is offered up to those of use who think in these terms.
|  | kevglynn
2006-10-31 09:10:31 | I'm surprised no one noticed this one... As x -> infinite, acceration must approach g (a -> g), so choice (D) is the only possibility. |  | clmw
2005-11-02 09:08:00 | One can remove some of the trig nastiness in the above solution by just noting that the tangetial acceleration equals the normalized tangent vector times g. Using x as our simple parameter, the y component of the tangent vector equals dy/dx=x/2 and the x component equals dx/dx=1. If we normalize this vector (1,x/2) and then multiply g by the normalized y component we get the answer pretty straightforwardly (without using sin/cos identities)
-Chris |  | maryrose
2005-11-01 13:08:02 | It can also be solved by noting the units and realizing that it cannot be zero or g. That leaves only D. |  | rreyes
2005-10-31 09:47:42 | nice solution! :)
let me just note that we can also answer this problem by method of elimination by observing that as x->\infty, a must -> g. this eliminates all answers except D. |  |
|
|
Comments |
casseverhart13
2019-09-19 02:59:13 | Some of your problem are actually sounds great. magician |  | ernest21
2019-08-10 03:09:42 | Thus, the application of dimensional analysis for eliminating answers only works for D. warship games |  | fredluis
2019-08-08 12:43:55 | I think when dealing with a signal of a single frequency (e.g., blue light), it only makes sense to talk about the phase velocity--you can\'t construct a \"group\" or wavepacket out of a single frequency signal. kitchen remodeling |  | joshuaprice153
2019-08-08 05:39:09 | Your current web-site is fairly quickly growing to be certainly one of my top feature. So, I just stumbled on creative weblog and I just need to state that this amazing is a nice blog post. Bless you pertaining to this kind of knowledge. towing service |  | calvin_physics
2014-03-27 15:04:37 | Just ignore the math. Take limits.
x = 0, acceleration must be zero.
x = big, acceleration must be g.
We only have two choices left. (D) and (E)
E gives wrong unit, it gives you an extra x.
D has the right unit. Bingo. |  | pranav
2012-11-02 22:23:53 | (same concept as one given...but simpler math)
Differentiating y w.r.t x gives:
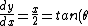)
Draw a right triangle, with one angle 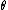 . .
Now label the side adjacent as "2", opposite as "x".
The hypotenuse becomes 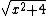 . .
Now we want the tangential acceleration, which would be the "g" multiplied by the cosine of the angle opposite to 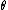 i.e. i.e. 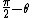 , since , since 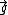 is downward parallel to the side we labeled "x" (i.e. the dot product basically) is downward parallel to the side we labeled "x" (i.e. the dot product basically)
Therefore, answer is:
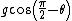 = g sin(\theta) = g \frac{(opposite)}{(hypotenuse)} = \frac{g x}{\sqrt{x^2+4}})
(D) |  | fkvkfdlek
2012-08-04 21:07:40 | can this be solved using lagrange multiplier?
I set up L' = L - ) and then was trying to rewrite tangential acceleration as and then was trying to rewrite tangential acceleration as 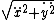
i cant quite finish the substitution to get the inside of the square root purely in terms of x |  | whatever
2011-11-11 15:28:18 | parametrization of the line is = (x,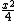 ), then taking its derivative with respect to x and dividing by it's length to get the tangential unit vector we get ), then taking its derivative with respect to x and dividing by it's length to get the tangential unit vector we get
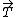 :=(1, :=(1,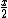 ) / ) / 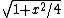
our vector for acceleration is
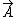 = (0,g) = (0,g)
the tangential component of acceleration is then their inner product
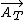 = = 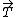 * * 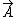 = gx/ = gx/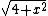 , D , D
|  | malianil
2011-11-05 05:52:47 | For those who are not inclined to solve it with trigonometric functions can take a snapshot drawing of the force diagram at arbitrary location (y,x) where rn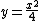 and then use euclidean geometry to find our that the Force component of the tangent is a function of x and is rn and then use euclidean geometry to find our that the Force component of the tangent is a function of x and is rn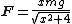 rnIt is simpler this way for me. rnIt is simpler this way for me. |  | nakib
2010-04-02 11:51:51 | (A) Lol!
(B) Of course not! The tangent is not pointing downwards.
(C) Wrong units.
(D) Right units, maybe correct. Also, 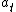 goes to goes to 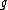 as as  goes to goes to  . .
(E) Wrong units.
(D) is the answer.
The rigorous solutions are beautiful, but are not feasible under GRE exam conditions...
archard
2010-06-05 18:04:39 |
The problem specifies the the coordinates are dimensionless units, so you can't eliminate C and E.
|
physicsworks
2010-07-09 09:40:46 |
nakib is right
when 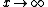 the acceleration must be the acceleration must be 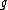 . There is only one appropriate choice for this, no matter what dimensions are given. . There is only one appropriate choice for this, no matter what dimensions are given.
|
Shahbaz Ahmed Chughtai
2012-06-09 22:51:44 |
Very Nice. GRE is designed to use common sense !!!
But I salute the website owners for such a hard work !
|
eighthlock
2013-08-11 13:07:06 |
Notice that the prompt states x and y are dimensionless units. Therefore you can't use dimensional analysis, because (D) and (E) have the same dimensions.
|
mike1999
2014-07-16 14:15:40 |
Actually, the problem specifies that x and y are dimensionless, so you can't 100% narrow it down like that (actually, perhaps if you substituted the dimensional quantity...). Anyway, you can also get it from limiting cases. As x->0, the answer should -> 0. As x -> inf, the answer should -> g (because the tangent gets infinitely steep). Thus D is correct.
|
|  | sirius
2008-11-05 19:37:19 | Here's an easier way:
Only (A),(B),and (D) have the correct units, first of all. You know that the particle is accelerating, and that its acceleration can't be greater or even equal to g, no matter what x is. Only (D) satisfies these conditions.
Why can't the acceleration be g? The track can never be vertical since y is constrained to a one-to-one function.
jmason86
2009-08-10 19:41:52 |
As Yosun pointed out below, the problem states that x and y are unit-less so you can't (technically) use dimensional analysis.
Limits (x->0 and x-> infinity) solves this whole problem without the need for units and it is still quick.
|
|  | p3ace
2008-05-15 06:11:52 | I apologize for what I just said. It came out wrong and I feel terrible after having reread it. What I meant to say was, if you want to know how to just crank out the answer, this is how I would do it. |  | p3ace
2008-05-15 06:08:15 | The process of elimination is great in a pinch on a test but it doesn't demonstrate any physics, or in this case math.
To me the most straight forward way to do this is:
The tangential direction is just the direction of r vector,
r=ix+jy=ix+j(x^2)/4.
r hat or the unit vector in the tangential direction is just r/magnitude, i.e.
r hat = [ix+j(x^2)/4]/{x^2+[(x^2)/4)]^2}^(1/2)
You can factor an x out of the denominator and cancel it with the x in the numerator, leaving
r hat = (i+jx/4)/[1+(x^2)/16]^(1/2)
Now dot the acceleration vector, a=jg with the unit vector in the tangential direction to get the tangential acceleration,
a tangential = g[(x/4)/(1+x^2/16)].
Now, to get the form in the answer, multiply through in the denominator by the 4. Inside the radical, it becomes a 16 so that you have,
a tangential = gx/[16+x^2)^(1/2), Wah, LA, choice D.
Sorry I'm not a latex jockey. To me this is radically simple, more so than the other solutions, just because this is what makes sense to me. I know that others see it differently and whatever works for you is a okay, so this is offered up to those of use who think in these terms.
neon37
2008-10-05 11:42:48 |
hey p3ace, you didnt quite get the answer though. The choice D has 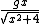 not not 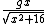 . .
|
ajkp2557
2009-10-27 11:18:17 |
Good approach, but note that the normalized tangent vector is the time derivative of the position vector (r-dot) divided by the magnitude of r-dot.
|
shen
2010-08-11 08:25:04 |
Actually u got the wrong tangential vector. It should be found using the gradient dy/dx.
r = [1, x/2]/(1+x^2/4)^1/2
You got the correct answer through a careless mistake that correctly make up for your wrong formulation. Cheers. You can check your answers.
|
|  | StrangeQuark
2007-06-16 09:25:22 | I did this problem by noting infinity conditions which in the test I am more then happy to do however in study I would like a more concrete answer, which I found on your site (thank you). However I have a question, you say that gravity is the only force acting, isn't there a constraining force from the track, i.e. a normal force that points perpendicular to the track that needs to be accounted for?
Jeremy
2007-11-11 11:24:55 |
I wondered about the official answer's omission of the normal force as well, but now I understand why it's not necessary. We only care about forces that have tangential components, and thus contribute to the tangential acceleration.
|
|  | kevglynn
2006-10-31 09:17:19 | Sorry, I'm an idiot and decided not to read before I wrote that :-)
Tried get rid of it, too, but it seems that you can't edit even your own posts. oh well |  | kevglynn
2006-10-31 09:10:31 | I'm surprised no one noticed this one... As x -> infinite, acceration must approach g (a -> g), so choice (D) is the only possibility.
carlospardo
2007-10-02 17:34:09 |
Yeah, and also studying units and considering that, obviously, it is not a constant
|
Richard
2007-10-31 12:28:05 |
That's how I did it.
There is a similar problem on another GRE exam...
the limiting technique works there as well.
|
Poop Loops
2008-11-02 16:23:51 |
Limits and boundary conditions are your friends!
A math teacher of mine used to tell me: The more math you do, the more room for error there is.
|
testtest
2010-11-11 18:45:16 |
That does not eliminate (E)
|
testtest
2010-11-11 18:46:34 |
Tzzzzz what am I saying... Time to go to bed! (yes it does eliminate E)
|
|  | kevglynn
2006-10-31 09:10:13 | I'm surprised no one noticed this one... As x -> infinite, acceration must approach g (a -> g), so choice (D) is the only possibility. |  | clmw
2005-11-02 09:08:00 | One can remove some of the trig nastiness in the above solution by just noting that the tangetial acceleration equals the normalized tangent vector times g. Using x as our simple parameter, the y component of the tangent vector equals dy/dx=x/2 and the x component equals dx/dx=1. If we normalize this vector (1,x/2) and then multiply g by the normalized y component we get the answer pretty straightforwardly (without using sin/cos identities)
-Chris
Jeremy
2007-11-11 11:57:51 |
I think this solution is much faster than the official one, so I thought I'd write out the equations. Let 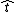 represent a unit vector in the tangential direction. We want to find the net tangential acceleration represent a unit vector in the tangential direction. We want to find the net tangential acceleration 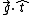 , or , or
=\frac{g dy}{\sqrt{(dx)^{2}+(dy)^{2}}}=\frac{g y'}{\sqrt{1+(y')^{2}}}=\frac{\frac{1}{2}g x}{\sqrt{1+\frac{1}{4}x^{2}}}=\frac{g x}{\sqrt{x^{2}+4}}) , ,
where 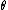 is the angle between is the angle between 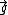 and and  . In the end, I guess this is the same idea expressed in the official solution, but without undue trigonometric hardship. . In the end, I guess this is the same idea expressed in the official solution, but without undue trigonometric hardship.
|
ajkp2557
2009-10-27 11:15:13 |
Great solution!
Side note for those that (like me) have forgotten: the tangent vector is the time derivative of the position vector. (Which makes sense physically, if you think about what the velocity vector is telling us.)
|
|  | clmw
2005-11-02 09:00:08 | |  | maryrose
2005-11-01 13:08:02 | It can also be solved by noting the units and realizing that it cannot be zero or g. That leaves only D.
yosun
2005-11-01 16:04:57 |
actually, maryrose, the problem gives "dimensionless units". thus one can't eliminate the other choices (other than 0 and g) that easily...
|
mrmeep
2008-09-07 18:46:07 |
The problem specifically says y and x are unitless, so does that thinking still hold?
|
|  | rreyes
2005-10-31 09:47:42 | nice solution! :)
let me just note that we can also answer this problem by method of elimination by observing that as x->\infty, a must -> g. this eliminates all answers except D. |  |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
